load
stockpiled
material
into
overhead
hoppers and trucks.
The production of any pit material
that
requires
crushing
and
screening
depends on the capacity of the processing
equipment used.
QUARRY OPERATIONS
Quarrying
involves
not
only
extraction
of
material
(rock)
but
also
crushing
and
screening
that
makes
the
rock
suitable
for
use
as
construction
material.
Quarry Terminology
Figure 5-10 shows the names of
various
quarry
features.
Overburden
is
the
waste
material
that
often
overlies
pit
or
quarry
sites.
Deposits
within
the waste materials are called spoil and
must
be
removed
before
excavation
of
the
construction
materials
lying
below.
Overburden
refers
to
loose
material
but
locally
it
may
include
solid
rock
lying
above
the
desired
material.
Burden
is
the
construction
material on the face of a quarry. The
floor of the quarry is the inside bottom
surface that marks the lower limit of
excavation.
Often
quarries
contain
one
or more working floors at various levels
above the final quarry floor. A quarry
wall is a more or less vertical surface
that
marks
the
lateral
limit
of
excavation. The face of a quarry is a
rock
surface
(usually
vertical)
from
which rock is to be excavated. The top
of the face is called the crest, and the
bottom is called the toe. A bench is a
steplike
mass
of
rock
behind
a
face
and below a working floor, Notice that
each bench has a face, toe, and crest.
Quarry Development
The
layout
of
a
quarry
should
provide a gravity flow of material from
the face to the crusher, from the crusher
to the storage bin, and from the bin to
the hauling equipment, as illustrated in
figure 5-11. A quarry laid out in this
manner assures that a maximum quantity of
rock can be processed with a minimum of
labor and equipment. In quarries laid out
on
the
gravity-flow
principle,
the
drainage
problem
is
practically
eliminated.
Military
quarries
are
generally
of
the
open-face
type
with
the
vertical
surface of the rock exposed. Depending
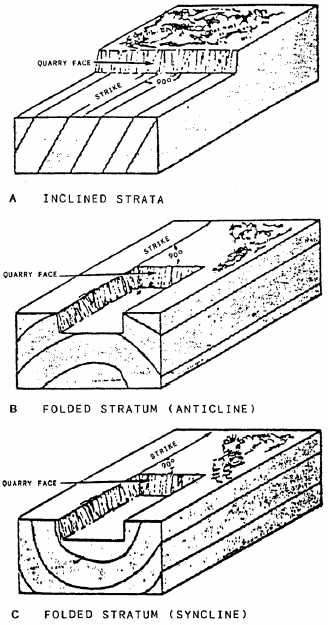
Figure 5-12.-Determining the direction of the
quarry face.
upon local conditions, they may be developed
by the single- or multiple-bench method.
Where the rock face is not exposed,
core samples should be taken in a grid
pattern so rock formations can be plotted,
and the lay of the strata, the quality and
quantity of the deposit, and depth of
overburden can be determined. Should a
rock
formation
be
jointed
or
stratified,
the layout of the quarry is determined by
the
strike
(direction)
of
the
formation;
that is, the face of the quarry must be
directed
at
right
angles
to
the
strike
(fig.
5-12).
This
ensures
a
vertical
or
near vertical face with less chance of
undercutting
the
face
and
creating
a
dangerous overhang.
5-13