After the base course has passed the compaction
test, prime the hole with a light application of asphalt,
which can either be sprayed or brushed on. The prime
material must be thin enough so that it can be applied
lightly.
NOTE: An excess of asphalt prime coat will flush
into the patch mix and causes bleeding.
The final step in the preparation of the hole is to
apply a tack coat to the vertical faces, as shown in figure
16-26.
Bituminous Materials Replacement
The first step in the replacement of the paving
materials is to obtain a sufficient quantity of material to
complete the project. Use a hot mix if possible because
it is stronger and lasts much longer.
To allow for
compaction when using a hot mix, you should overfill
the area approximately 40 percent of the pavement
thickness. When a cold mix is used, it should be spread
and rolled in layers with each layer not to exceed 1 1/2
times the maximum aggregate size in the mix. When
cold mix is spread, keep the material as level as possible
to prevent segregation. Both hot and cold mixes can be
spread by grader, by paver, or by hand, depending on the
size of the repair.
Compaction of bituminous materials is done with
steel-wheel rollers and pneumatic-tired rollers on larger
areas, or with vibrator tampers, vibratory patch rollers,
and hand tampers on smaller areas. Compaction is an
important part of the patching operation. The rolling
operation on hot mix should begin immediately after the
material is placed. Cold mix should be rolled after
Figure 16-26.-Tack coat application to the vertical faces.
16-22
proper aeration of the material. The edges of the patch
should be rolled first. This seals the edges and prevents
the material from dishing out and water from
infiltrating. When cold mix is used, the patch may have
a porous surface and require waterproofing. This can
be done by applying a sand seal or by applying a thin
layer of portland cement and tamping it in.
Obtaining a smooth riding surface requires care.
Too many patches are built as mounds that result as
bumps in the road A straightedge should be used as a
guide to finish the patch. The patch should not be lower
than the rest of the pavement. Instead, it should be level
with or one-eighth inch higher than the surrounding
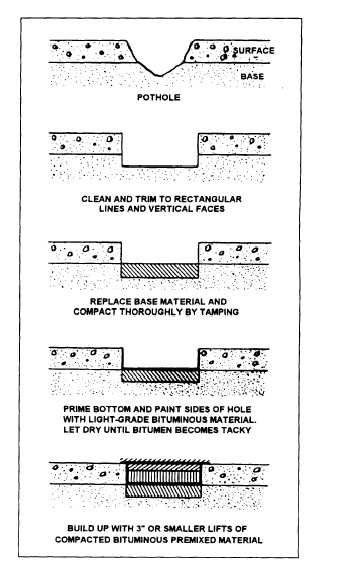
area. Figure 16-27 shows the steps in patching a
pothole.
Figure 16-27.-Steps in patching a pothole.