be reset. The rodman reads the target to feet, tenths,
and hundredths of the nearest foot gradation below the
horizontal quadrant separation line of the target.
Equipment Operator’s seldom use the vernier scale in
earthwork operation.
LEVELING
The vertical distance, measured during leveling,
is the difference of elevation between two points. The
term elevation refers to the height of a point or a
particular spot above or below a reference line, called
a datum or datum plane.
Datum are of two general types: actual and
assumed. An actual datum is mean sea level (fig.
15-46). An assumed datum plane is an imaginary level
surface assumed to have an elevation of zero. It is used
as a convenience in leveling procedures.
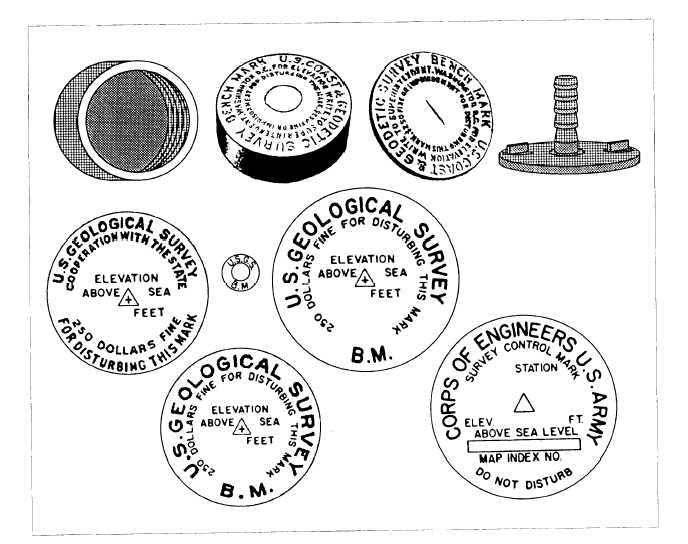
A reference point whose elevation is known and
marked is called a bench mark (B.M.). It is used
either as the starting point in leveling or as a point of
closure in checking the accuracy of your work.
Bench Marks
Bench marks are classified as temporary or
permanent. Temporaary bench marks (T. B. M.) are
established for the use of a particular job and are
retained for the duration of that job. Throughout the
United States, a series of permanent bench marks has
been established by various governmental agencies.
These identification markers are set in stone, iron pipe,
or concrete and are sometimes marked with the
elevation above sea level. Typical markers are shown
in figure 15-47.
Figure 15-47.—Federal bench marks.
15-27