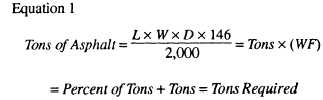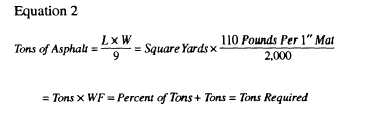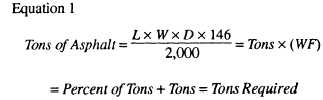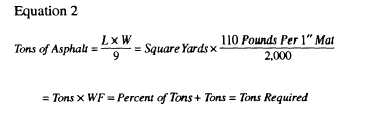forth laterally with a grader before being spread and
compacted. This action speeds up setting or curing.
Always round your answer to the next higher
number. In this case, 1478.4 is rounded to 1479 gallons.
TYPES OF ASPHALT PAVEMENT
CONSTRUCTION
Two major types of asphalt pavement construction
are in use today: plant mix construction (so-called
because the mixture is prepared in a central mixing
plant) and mixed-in-place construction (so-called
because the mixture is mixed on the area to be paved).
PLANT MIX CONSTRUCTION
L =
Asphalt-paving mixtures, prepared in a asphalt
mixing plant, are known as plant mixes. Plant mix
asphalt concrete is considered the highest quality plant
mix. It consists of well-graded, high-quality aggregate
and asphalt cement.
The asphalt and aggregate are
heated separately from 250°F to 325°F, carefully
measured and proportioned, then mixed until the
aggregate particles are coated with asphalt. The hot
mixture, kept hot during transit, is hauled to the
construction site where it is spread on the roadway with
an asphalt-paving machine. The smooth layer from the
paver is compacted by rollers to proper density before
the asphalt cools.
W =
D =
146 =
Asphalt concrete is but one of a variety of
hot-asphalt plant mixes.
Other mixes, such as sand
asphalt and coarse-graded mixes, are prepared and
placed in a similar manner; however, each has one
common ingredient, which is asphalt cement.
Asphalt mixes, containing emulsified or cutback
asphalt, may also be prepared in asphalt mixing plants.
The aggregate may be partially dried and heated or
mixed as it is withdrawn from the stockpile. These
mixes are usually refered to as cold mixes, even though
heated aggregate may have been used in the mixing
WF =
2,000 =
process.
Both asphalt mixtures, made with emulsified
asphalt and some cutback asphalts, can be spread and
compacted on the roadway while quite cool. Such
mixtures are called cold-laid asphalt plant mixes
They are hauled and placed in normal warm weather
temperatures. These mixtures, after being placed on the
roadway, are sometimes processed or worked back and
Compute Plant-Mix Materials
Several methods are used to calculate the amount of
hot-mix material, required for paving projects; however,
when the weight of a hot mix per square yard or cubic
foot is not known, two equations are used in the NCF to
compute the number of tons of asphalt, required for a
project. These equations are as follows:
length of project in feet.
width of project in feet.
depth or thickness of compacted mat. You
must change inches into feet by dividing the
number of inches by 12 (inches in 1 foot).
For paver screed height, add 1/8 inch for
each inch of the mat to be paved. (Example:
For a 2-inch mat, two blocks of wood 2 1/4
inches thick will be required to set under the
screed.) The blocks must be thicker than
the finished compacted mat to allow for
additional compaction by rollers.
This number represents the approximate
weight of 1 cubic foot of compacted
hot-mix asphalt.
This number can vary
from 140 to 160 pounds; however,
146 pounds equals the 110 pounds per
square yard per l-inch depth of asphalt used
in the second equation for figuring tons
require for asphalt. (See table 16-2.)
Waste factor equals 5% or .05, or 10% or
.10, depending on the experience of the
screed operators and handwork required on
the project.
2,000 pounds is equal to one ton; therefore,
you must divide the total weight of material
by 2,000, giving tons required.
16-9