Emergency Treatment of Burns
Classification of Burns
Burns are classified in several ways: by the extent
The degree of the burn, as well as the skin area
of the burned surface, by the depth of the burn, and by
involved, determines the procedures used in the
the cause of the burn. The extent of the body surface
treatment of burns. Large skin areas require a different
burned is the most important factor in determining the
approach than small areas. To estimate the amount of
seriousness of the burn and plays the greatest role in the
skin area affected, the extent of burned surface, the
victim's chances of survival.
"Rule of Nines" (fig. 1-5) is used. These figures aid
in determining the correct treatment for the burned
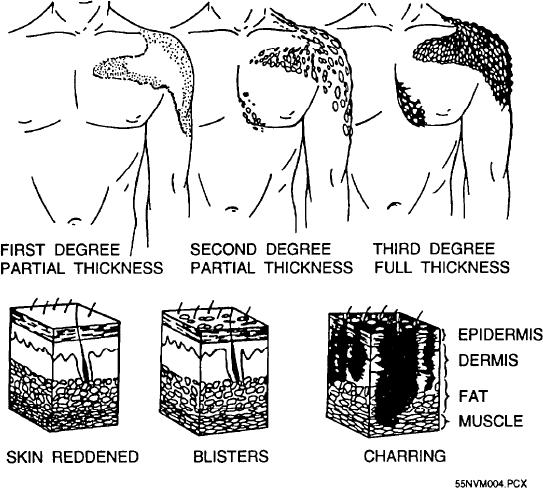
Burns may also be classified as first, second, or
person.
third degree, based on the depth of skin damage (fig.
1-4). First-degree burns are mildest. Symptoms are
As a guideline, consider that burns exceeding 15
reddening of the skin and mild pain. Second-degree
percent of the body surface will cause shock; burns
burns are more serious. Symptoms include blistering of
exceeding 20 percent of the body surface endanger life;
the skin, severe pain, some dehydration, and possible
and bums covering more than 30 percent of the body
shock. Third-degree burns are worst of all. The skin is
surface are usually fatal if adequate medical treatment
destroyed and possibly the muscle tissue and bone in
is not received.
severe cases. The skin may be charred or it may be
white or lifeless. This is the most serious type of burn,
Minor burns, such as first-degree burns over less
as it produces a deeper state of shock and will cause
than 20 percent of the body area and small
more permanent damage. It is usually not as painful as
second-degree bums, do not usually require immediate
a second-degree burn because the sensory nerve endings
medical attention unless they involve the facial area.
have been destroyed.
Figure 1-4.--First-, second-, and third-degree burns.
1-14