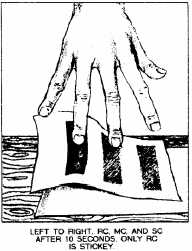
Figure 8-24.–Smear test of asphalt cutback.
Smear Test
The smear test is used to separate
an RC from an MC or SC. The test is
primarily based on the fact that RCs are
cutback with a highly volatile material
(naphtha or gasoline). You can determine
whether a sample is an RC or not by
smearing some of the sample in a thin
layer on a nonabsorbent surface, such as a
piece
of
glazed
paper.
The
volatile
substance evaporates within a few minutes
and the surface becomes so tacky that when
touched,
the
specimen,
paper
and
all,
sticks to your fingers and can be lifted
into the air (fig. 8-24).
Checking the reverse side of the
paper, you will find that the RC did not
penetrate through the paper as MCs or SCs
do. MCs and SCs on smear tests remain
fluid and oily for time periods that vary
from hours to days, depending on the type
and grade of material. If an 800 or 3,000
grade MC or SC is present, they may become
sticky in a few minutes since there is
such a small amount of cutterstock in
them.
When
such
a
viscous
grade
is
present,
it
is
well
to
confirm
the
identification of the sample by a prolonged
smear test. Generally, the MCs and SCs will
penetrate through the paper while the RCs
will
not.
You
can
determine
this
by
observing the back side of the paper.
In a prolonged smear test, a thin
smear is made on nonabsorbent paper and
allowed to cure completely. If the viscous
cutback
is
all
RC-3000,
it
will
cure
completely in about 3 hours. When the spot
has cured completely (the cutterstock has
almost
all
evaporated),
the
smear
will
be almost pure asphalt cement (AC) and
will be hard and no longer sticky. If
the viscous sample were an MC or SC-
800 or 3,000, the spot would still be
Figure 8-25.—Stone-coating test for emulsions.
uncured and, therefore, very sticky, even
after 24 hours, while the RC smear will
have become a hard, glazed spot.
Heat-Odor Test
A
heat-odor
test
is
used
to
distinguish
between
medium-curing
and
slow-curing asphalt cutback by identifying
the cutter stock as kerosene, fuel oil, or
diesel oil. A sample of the material is
heated in a closed container to retain the
vapors. (CARE MUST BE TAKEN TO AVOID THE
USE OF TOO MUCH HEAT). Medium-curing
asphalt cutback will have a strong odor of
kerosene. Slow-curing asphalt cutback will
lack the kerosene odor, but a faint odor
of motor oil may be present.
Field Penetration Test
The
field
penetration
test
is
performed
to
determine
the
approximate
hardness of the asphalt, not to pinpoint
the exact penetration number for it. To
determine if the number falls in the hard,
medium, or soft group is sufficient.
To perform this test, attempt to
push a sharpened pencil or nail into the
container
of
asphalt
(at
about
77°F),
using
a
firm
strong
pressure
of
approximately 10 pounds. If only a slight
penetration
is
made
with
considerable
difficulty,
a
hard
asphalt
cement
is
present.
When
the
penetration
is
made
slowly
but
without
great
difficulty,
a
medium asphalt cement is present. If the
penetration is made with ease, the asphalt
cement is a high penetration scale (a soft
AC).
Stone-Coating Test
When a material has been tested and
found to be an emulsion, the stone-coating
test is performed (fig. 8-25). This test is
conducted to determine if the emulsion is a
8-26