Table 16-1.—Recommended Uses of Various Asphalt Grades
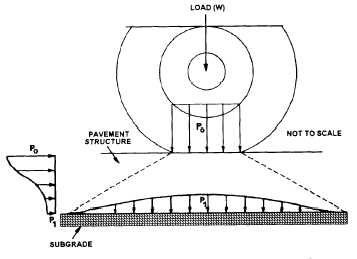
Figure 16-3.-Spread of wheel load through the pavement
structure.
asphalt, and one or more supporting courses, which may
be of the following types:
1. Asphalt base, consisting of asphalt-aggregate
mixtures (macadam)
2. Crushed stone (rock), slag, or gravel
3. Portland cement concrete
4. Old brick or stone block pavements
Asphalt pavement structure consists of all courses
above the prepared foundation. The upper or top layer
is the asphalt-wearing surface.
Essential Properties of Asphalt-Wearing
Surface
The surface of an asphalt pavement, exposed to
vehicular traffic, must be tough to resist distortion and
to provide a smooth riding surface. It must be
waterproof and sloped to shed surface water to the
roadside and protect the entire asphalt pavement
structure and the foundation from the erosive effects of
moisture. It must resist wear, caused by traffic, and still
retain necessary anti-skid properties. It must also be
bonded to the layer or course beneath it.
16-3