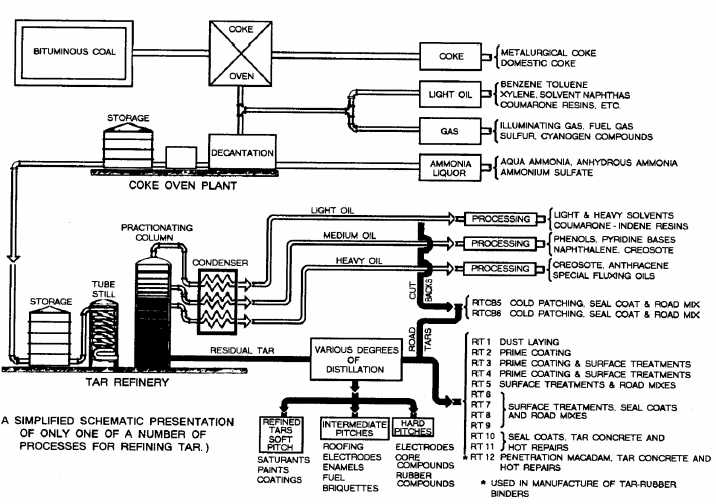
Figure 8-20.—Tars obtained from distillation of bituminous coal.
The viscosity grades range from 1 (least
fluid) to 3 (most fluid).
Use of Asphalt Emulsions
Emulsions
are
used
for
surface
treatment, road and plant mixes, and crack
and joint filling. The mixing grades can
be mixed unheated with damp aggregate.
They are preferred over asphalt cutback
when the aggregate is very damp. Cationic
emulsions coat damp aggregate better than
anionic
emulsion.
Recommended
use
of
emulsions
depends
on
setting
rate
and
mixing
ability.
At
water-freezing
temperatures,
asphalt
emulsions
do
not mix well since the emulsion will
separate
from
the
water.
Also,
emulsions
have
a
relatively
short
shelf
life
and
tend
to
break
while
still
in
their
unopen
drums.
Tars
Tars are obtained from the distillation of
bituminous coal (fig. 8-20) and are seldom used in
the NCF. A road tar is designated by the symbol RT
and is manufactured in 12 grades of viscosity
(table 8-5). RT-1, RT-2, and RT-3 are PRIMING
OIL. RT-4 through RT-7 are called COLD TARS
because they are fluid enough to be mixed and
applied at relatively low temperatures. RT-8
through RT-12 are called HOT TARS because they
are solid enough to require high temperatures for
mixing and applying.
The symbol RTCB refers to ROAD TAR
CUTBACK. RTCBs are manufactured only in
viscosity grades 5 and 6. Coal distillate,
such
as
benzene
or
a
solution
of
naphthalene in benzol, may be used to
cutback the heaviest grades of road tar to
produce both grades of road tar cutbacks.
The viscosity grades of road tars and road
tar
cutbacks
can
be
compared
to
the
8-22