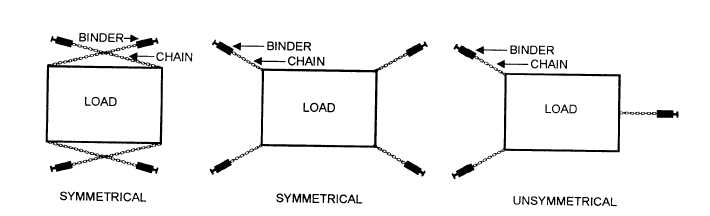
Figure 7-33.—Symmetrical tie-down pattern.
should be shaped to fit snugly against the cargo and
should be secured to the deck of the trailer to prevent
the cargo from moving. Bracing is also used to prevent
movement of the cargo. Bracing is placed from the
upper part of the cargo to the floor and/or walls of the
cargo compartment.
Because cargo loads have a tendency to shift, a
common rule of thumb is to inspect the cargo and the
securing devices before departing and within 25 miles
after beginning a trip. Always check the cargo and
securing devices as often as necessary during a trip to
keep the load secured. Inspect the cargo and securing
devices after you have driven for 3 hours or 150 miles
and after every break taken during the trip.
LOOSE MATERIAL.— Dump trucks are often
used to haul loose material. Soil, aggregate, and sand are
examples of cargo that is categorized as loose material.
When you are operating dump trucks, be sure that no
part of the load can fall off your truck when making
turns. You should stop loading before it reaches the top
of the side or end gate. Dirt spilled in curves and turns
creates driving hazards and should be cleaned up daily.
Another hazard created by loose material is a broken
windshield caused by aggregate falling from dump
trucks.
NOTE: In some states and on some deployment
locations, it is a requirement that all loose material loads
carried in dump trucks must be covered.
BUILDING MATERIAL.— When loading steel,
lumber, or anything that must be unloaded with a forklift
or crane, you should place 4 by 4 timbers or pallets
under the load. This helps get forks or cables in and out
from under the load
RESTRAINTS.— Loads must be secure enough to
prevent movement in any direction, which means
movement forward, aft, vertically, and horizontially.
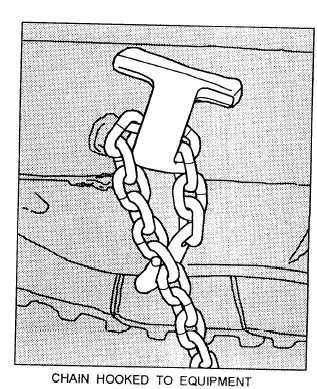
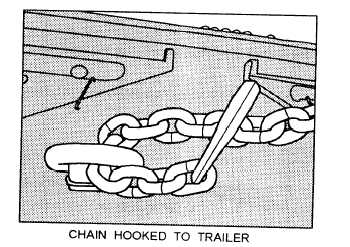
Figure 7-34.—Chains properly hooked on the equipment and
trailer tie-down eyes.
7-28