Figure 2-1.—Geometric orientation of the LM2500 GTE
The following section discusses the borescope
procedures used to inspect the LM2500 GTE. The
inspection procedures and the knowledge gained from
damage evaluation may also be applied to the borescope
inspection of the Allison 501-K17 GTE.
GENERAL INSPECTION PROCEDURES
It is a good engineering practice to review the
machinery history of an engine before you conduct an
inspection Various component improvement programs
will eventuallyy effect all engines in service. A rebuilt or
modified engine may contain improved parts that differ
from the original. An example of this is the first-stage
compressor midspan damper that may have its original
coating, an improved coating, or a carboloy shoe welded
on at the midspan damper interface. If you review the
machinery history, you will discover the status of those
parts that have been changed or modified.
Assuming that the engine history is normal and
FOD is not suspected, you should be aware of the
following factors when conducting a borescope
inspection:
Know your equipment.
Locate all inspection areas and ports.
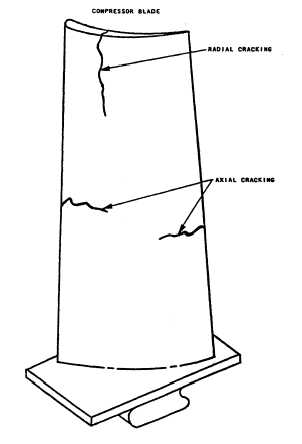
Figure 2-2.—Example of radial and axial cracking.
2 - 2