l
l
l
l
l
CHAPTER 12
INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE
CHAPTER LEARNING OBJECTIVES
Upon completion of this chapter, you should be able to do the following:
Explain the principles of a combustion engine.
Explain the process of an engine cycle.
State the classifications of engines.
Discuss the construction of an engine.
List the auxiliary assemblies of an engine.
The automobile is a familiar object to all of us. The
engine that moves it is one of the most fascinating and
talked about of all the complex machines we use today.
In this chapter we will explain briefly some of the
operational principles and basic mechanisms of this
machine. As you study its operation and construction,
notice that it consists of many of the devices and basic
mechanisms covered earlier in this book.
COMBUSTION ENGINE
We define an engine simply as a machine that
converts heat energy to mechanical energy. The engine
does this through either internal or external combustion.
Combustion is the act of burning. Internal means
inside or enclosed. Thus, in internal combustion
engines, the burning of fuel takes place inside the
engine; that is, burning takes place within the same
cylinder that produces energy to turn the crankshaft. In
external combustion engines, such as steam engines, the
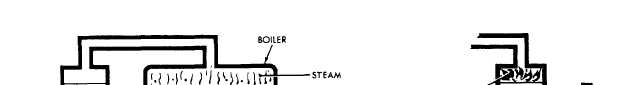
burning of fuel takes place outside the engine. Figure
12-1 shows, in the simplified form, an external and an
internal combustion engine.
The external combustion engine contains a boiler
that holds water. Heat applied to the boiler causes the
water to boil, which, in turn, produces steam. The steam
passes into the engine cylinder under pressure and
forces the piston to move downward. With the internal
Figure 12-1.-Simple external and internal combustion engine.
12-1