Whether the causes of broken valve heads are
mechanical deformation or metal fatigue, you must take
every precaution to prevent their occurrence. If a valve
head breaks loose, be sure to make a thorough inspection
of all associated parts before you replace the valve.
ROCKER ARMS AND PUSHRODS
The principal trouble that rocker arms and pushrods
may have is WEAR, which may occur in bushings, or
on the pads, end fittings, or tappet adjusting screws.
Worn rocker arm bushings are usually caused by
lubricating oil problems. A bushing with excessive wear
must be replaced. When installing a new bushing, you
usually need to use a reamer for the final fit.
Wear at the points of contact on a rocker arm is
generally in the form of pitted, deformed, or scored
surfaces. Wear on the rocker arm pads and end fittings
is greatly accelerated if lubrication is insufficient or if
there is excessive tappet clearance. Pushrods are usually
positioned to the cam followers and rocker arms by end
fittings. The pads are the rocker arm ends that bear the
valve stem or valve stem cap. When the tappet clearance
is excessive, the rods shift around, greatly increasing the
rate of wear of both the rocker arm and the rod contact
surfaces. Worn fittings necessitate the replacement of
parts. Continued use of a poor fitting and worn pushrod
is likely to result in further damage to the engine,
especially if the rod should come loose.
Worn tappet adjusting screws and locknuts usually
make maintaining proper clearances and keeping the
locknuts tight very difficult. Wear of the adjusting
screws is usually caused by loose locknuts, which allow
the adjusting screw to work up and down on the threads
each time the valve is opened and closed. To prevent this
wear, tighten the locknuts after each adjustment and
check the tightness at frequent intervals.
If the threads are worn, replace the entire rocker
arm. Do NOT attempt to repair the threads or to use a
new tappet adjusting screw except in cases of
emergency.
The adjustment of the rocker arm assembly consists
chiefly of adjusting the tappets for proper running
clearance. The valve clearance for both intake and
exhaust valves should be readjusted after overhaul. The
procedure for adjusting the rocker arm tappets of a
typical 4-stroke cycle engine is as follows:
1. Rotate the crankshaft and move the piston whose
tappets you plan to adjust to top dead center of the
compression stroke.
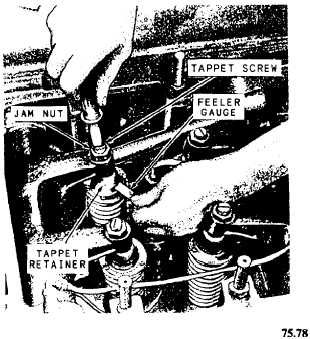
2. Loosen the locknut (jam nut) on the tappet
screw, and insert a screwdriver in the slot of the screw.
3. Insert a feeler gauge of the proper thickness
between the tappet bearing and the end of the valve stem.
4. Tighten the tappet screw (fig. 3-16) until the
feeler gauge will just slide freely between the bearing
and the valve stem.
5. lighten the jam nut and check the clearance. The
jam nut has a tendency to increase the clearance when
tightened; therefore, ALWAYS check the clearance after
you tighten the jam nut.
The procedure just outlined is a preliminary, or cold
engine check. Check and readjust the clearance, if
necessary, after the engine has been in operation for a
short time and has reached the normal operating
temperature. The manufacturer’s technical manual will
give the recommended valve clearances for a specific
make and model of engine and will indicate whether the
clearances given apply to cold or hot engines.
CAM FOLLOWERS AND LASH
ADJUSTERS
Regardless of the type of cam follower, wear is the
most common trouble. Worn rollers will usually develop
holes or pit marks in the roller surfaces. The mushroom
type may develop a shallow channel when the cam
Figure 3-16.—Adjusting valve clearance.
3-12