injection system. The air and fuel then mix in the
combustion chamber (fig. 1-8).
4. The engine speed and the power output of a
diesel engine are controlled by the quantity of fuel
admitted to the combustion chamber. The amount of air
is constant. On the gasoline engine, the speed and power
output is regulated by limiting the air and fuel mixture
entering the engine (fig. 1-9).
A diesel engine is much more efficient than a
gasoline engine, such as the diesel engine does not
require an ignition system due to the heat generated by
the higher compression, the diesel engine has a better
fuel economy due to the complete burning of the fuel,
and the diesel engine develops greater torque due to the
power developed from the high-compression ratio.
The strokes that make up the four-stroke cycle of a
diesel engine follow.
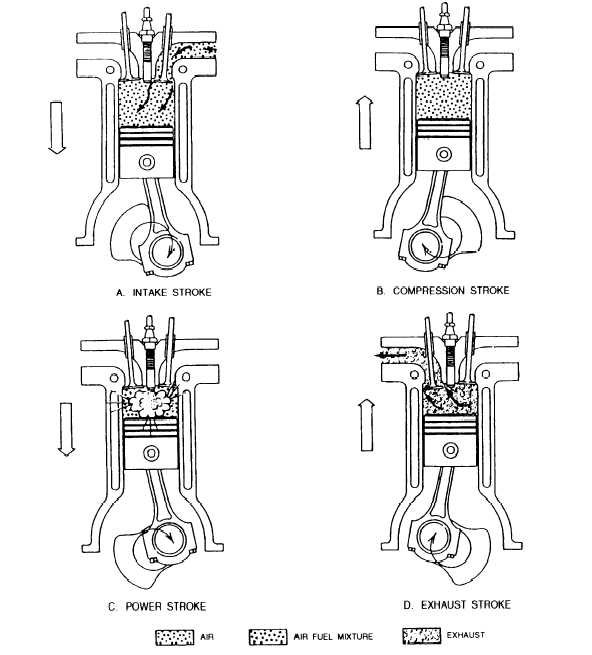
DIESEL ENGINE INTAKE STROKE.— The
piston is at top dead center at the beginning of the intake
stroke, and, as the piston moves downward, the intake
valve opens. The downward movement of the piston
draws air into the cylinder, and, as the piston reaches
bottom dead center, the intake valve closes (fig. 1-10,
view A).
Figure 1-10.—Four-stroke cycle diesel engine.
1-7