follows: intake, compression, power, and exhaust. A
cycle occurs during two revolutions of the crankshaft.
INTAKE STROKE. — The intake stroke begins at
top dead center, and as the piston moves down, the
intake valve opens. The downward movement of the
piston creates a vacuum in the cylinder, causing a fuel
and air mixture to be drawn through the intake port into
the combustion chamber. As the piston reaches bottom
dead center, the intake valve closes.
COMPRESSION STROKE.— The compression
stroke begins with the piston at bottom dead center and
rising up to compress the fuel and air mixture. Since both
the intake and exhaust valves are closed, there is no
escape for the fuel and air mixture, and it is compressed
to a fraction of its original volume. At this point, the fuel
and air mixture is ignited.
POWER STROKE.— The power stroke begins
when the fuel and air mixture is ignited, burns and
expands and forces the piston down. The valves remain
power stroke ends as the piston reaches bottom dead
center.
EXHAUST STROKE.— The exhaust stroke
begins when the piston nears the end of the power stroke
and the exhaust valve is opened. As the piston moves
upward towards top dead center, it pushes the burnt
gases, resulting from the ignition of the fuel and air
mixture, out of the combustion chamber and through the
exhaust port. As the piston reaches top dead center,
ending the exhaust stroke, the exhaust valve closes, and
the intake valve opens to begin the intake stroke for the
next cycle.
Four-Stroke Cycle Diesel Engine
The four-stroke diesel engine is similar to the four-
stroke gasoline engine. They both follow an operating
cycle that consist of intake, compression, power, and
exhaust strokes. They also share similar systems for
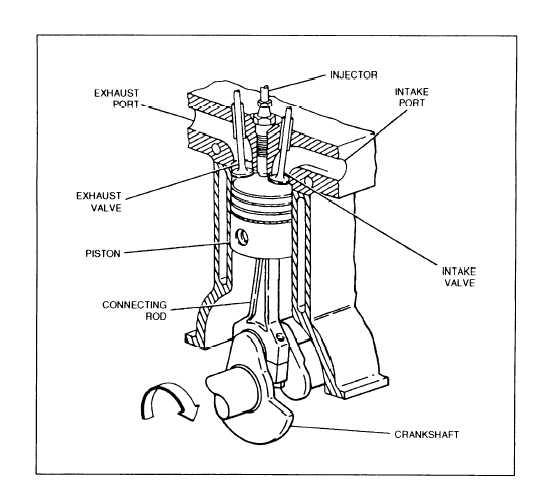
intake and exhaust valves. The components of a diesel
closed so that all the force is exerted on the piston. The
engine are shown in figure 1-6.
Figure 1-6.—Four-stroke cycle diesel engine.
1 - 4