The common fraction is a simple method of
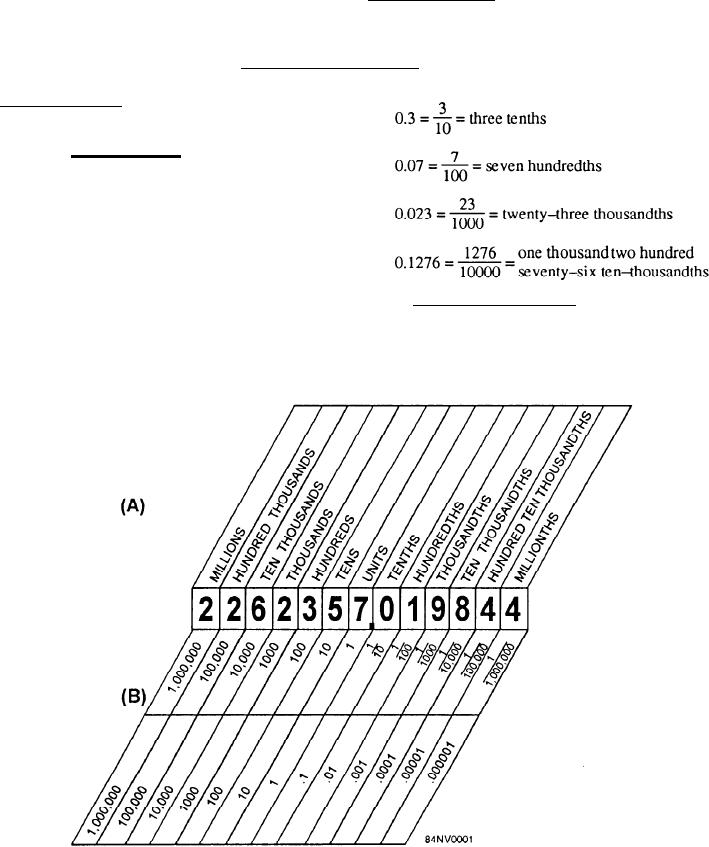
one-tenth the value of the preceding place. Notice in
views A and B that the units place is the center of the
expressing the division of a whole number or object.
system and that the place values proceed to the right or
Fractions show one or more parts divided into any
left by powers of ten. Ten on the left is replaced by
number of equal parts. Examples are dividing 1 inch
tenths on the right, hundreds by hundredths, thousands
into four equal parts or dividing a line into four equal
by thousandths, and so on. Notice that each decimal
parts. These equal parts are expressed as increments of
fraction begins with a period. This period is called a
one--fourth. You know that four increments equal the
decimal point. To call attention to the decimal point,
whole number or object. You can write any part less
we usually begin the decimal fraction with a zero.
than the whole as a common fraction, such as l/4 or 3/4.
Examples of decimal fractions, their equivalent
The common fraction contains two parts--the
common fractions, and how you read them are as
denominator and the numerator. The denominator
follows:
shows how many equal parts the whole divides into.
The numerator shows the number of equal parts being
considered.
5 (Numerator)
Example:
8 (Denominator)
DECIMAL FRACTION
A decimal fraction is a fraction whose denominator
is 10 or some multiple of 10, such as 100, 1,000, or
10,000. Decimal fractions differ from common
A mixed decimal is an integer and a decimal
fractions in that the denominators are not written but
fraction combined. We use a decimal point to separate
are expressed by place value. Figure 14-1, views A and
the integer portion from the decimal fraction portion.
B, shows a place value chart. As we proceed from left
to right in place value, the value of each place is
Figure 14-1.--Place value chart.
14-2

