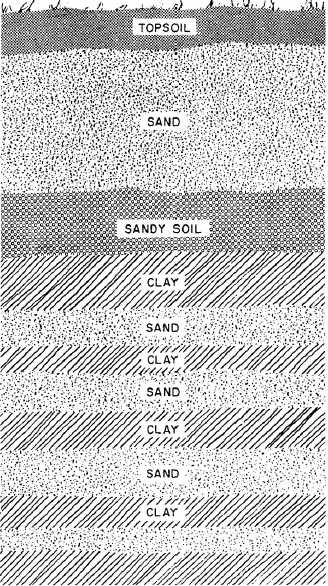
Figure 9-2.-Geologic formation of earth layers.
and
sandstone,
are
huge
reservoirs
of
groundwater. Sedimentary rock formations are
among the most common and productive of
all aquifers, and when found in sandy or
gravel formations are easy to drill.
Igneous and metamorphic formations are
both viewed as a group of hard, dense
rocks.
Unless
highly
fractured
and
occurring
close
to
the
earth’s
surface,
they
contain
far
less
water
than
sedimentary rocks. The recovery of water from
solid rock depends on the existence of
many cracks, fissures, or crevices in the
rock.
Extremely
fine
deposits
of
sedimentary
materials
usually
produce
little water. Although highly porous, they
are relatively impermeable.
Topographical
features
created
by
water action offer an excellent chance for
the recovery of groundwater at relatively
shallow depths. Alluvial sedimentary deposits
are
the
most
productive
formations
for
groundwater.
The
word
alluvial
means
deposited by water. Such features include
the
following:
alluvial
valleys
that
are
rather extensive in area and are the sites
of ancient rivers or the flood plains of
active rivers; alluvial fans that are an
accumulation of sediments at the base of
mountains,
deposited
where
drainage
streams fan out; and alluvial basins that are
essentially
structural
troughs
created
by
a rim of mountains and glacial outwash.
GROUNDWATER EXPLORATION
Where extensive groundwater exploration
has not occurred, maps, official documents,
unofficial documents, and native experience
must be used to obtain a fairly reliable
indication
as
to
a
groundwater
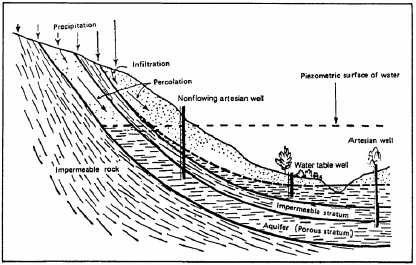
Figure 9-3.—Types of aquifers.
9 -3