resource
of
a
particular
area.
The
information
available
normally
will
give
you
an
idea
as
to
the
geological
conditions,
such
as
terrain
and
type
material, approximate depth of an aquifer
or series of aquifers, quantities of water
that
may
be
expected
during
different
seasons of the year, average depth of the
water table, and drilling procedures and
problems that may be encountered.
Access to maps and publications is
usually
through
hydrographic
offices
either
on
a
state
or
national
level,
offices of the United States Coast and
Geodetic
Survey,
or
its
equivalent
in
other
countries,
geological
or
university
archives,
battalion
engineering
offices,
or
native
drillers.
When very little is known about the
water resources in a particular area, the
most valuable clues may come from an
inspection
of
the
outcropping
of
rock
format ions. You may need to verify your
conclusions by exploratory drilling, which is
the surest way to establish the existence
of
water-bearing
formations.
Exploratory
drilling
is
usually
initiated as part of the groundwater study
of an area before construction of water
wells at a particular site.
WELLS
Wells are classified into five methods
of construction. The methods are as follows:
dug, bored, jetted, driven, and drilled wells, Each type of
well has certain advantages and limitations;
and the type of well to be developed depends
upon
the
ease
of
construction,
storage,
capacity, limitations as to formations it can
penetrate,
and
ease
of
safeguarding
it
against
pollution.
A dug well is one in which the
excavation is Made by the use of picks,
shovels,
spades,
or
digging
equipment,
such as sand buckets or clamshell buckets.
A bored well is one in which the excavation
is made by the use of hand or power augers.
A jetted well is one in which the
excavation is made by the use of a high-
velocity jet of water.
A driven well is one which is
constructed by driving a pointed screen,
referred to as a drive point, into the
ground. Casings or lengths of pipes are
attached to the drive point as it is being
driven into the ground.
Dug, bored, jetted, and driven wells are
relatively
shallow,
Generally,
they
are
less than 100 feet deep and may be
constructed with hand tools. Drilled wells
in the NCF are normally drilled to the
depth of 1,500 feet and are constructed
with portable well drilling machines.
ROTARY DRILLING
When using a hand drill to bore a
hole, you press the cutting tool or bit
into
the
material
to
be
bored.
The
material is cut as you turn the bit by
means of the drill handle. During the
drilling
process,
chips
of
the
cut
material are carried to the top of the
hole by the flutes of the bit. A rotary
drilling rig operates on the same principle,
except for the method of raising the cut
material, This material is washed to the
surface by a fluid substance instead of
being carried by the bit itself. The bit
of a rotary drilling rig is attached to the
lower end of the drill pipe.
The methods of drilling for water
are referred to as rotary mud or rotary air
drilling. Rotary mud drilling is currently the
most common method used to drill wells and
is used where ground formations are loose
and unconsolidated. Mud drilling is also
used in consolidated formations but is not
very efficient. The rotary air drilling method
is preferred when ground formations are
consolidated.
A
limitation
of
the
air
drilling method is the cfm output of the air
compressor.
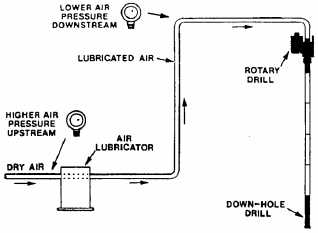
When rotary mud or rotary air drilling
operations
are
being
conducted
and
a
formation that is hard to penetrate is
encountered, the down-hole-drilling hammer
attachment can be used. The down-hole-
drilling hammer attaches to the lower end
of the drill pipe and rotates as well as
hammers (short rapid blows) against the
hard formation (fig. 9-4). To use the
Figure 9-4.-Down-hole-drilling (DHD).
9-4