Cross Sections
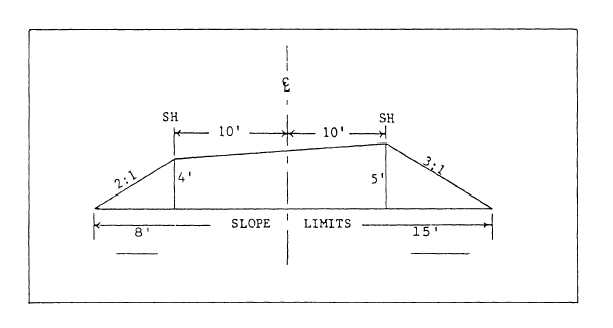
A cross-sectional view (fig. 15-16) that is given
for a road project is a cutaway end view of a proposed
station between the left slope and the right slope.
Typical cross sections are plotted at any intermediate
place where there is a distance change in slope along
the center line where the natural ground profile and
grade line correspond. The cross section displays the
slope limits, the slope ratio, and the horizontal
distance between centerline stakes and shoulder
stakes. It also shows the vertical distance of the
proposed cut or fill at the shoulder and centerline
stakes.
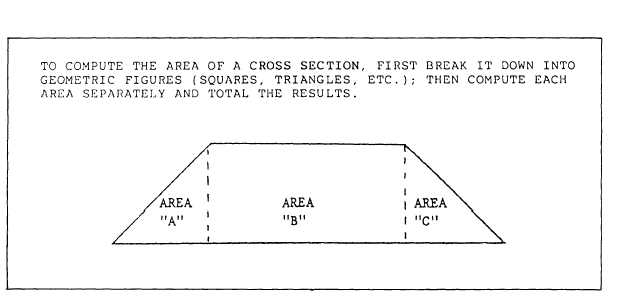
To compute the area of a cross section, you must
first break it down into geometric figures (squares,
triangles, etc.). (See fig. 15-17.) Compute each area
separately, then total the results to obtain the total
square feet.
Figure 15-16.—Cross section.
Figure 15-17.—geometric sections of a cross section.
15-13