plywood sheets is 4 feet wide by 8 feet long, though
fiber faces that provide better painting surfaces and
smaller and larger sizes are available. Because of
better wearing qualities.
the cross-grain effect, splitting plywood is very
difficult and shrinking and swelling are rare.
Because of the conditions of its manufacture,
plywood is dry when received. It should be stored
in a closed shed. For long storage, a heated storage
The development of special glues and bonding
area is recommended.
materials has made plywood highly resistant to
water. It was widely used during World War II and
is still in use in the Navy.
Plywood is commonly stacked in solid piles.
Under humid conditions, edges swell because of
Two basic grades of plywood are interior and
exposed end grain. This swelling causes dishing,
exterior. Interior plywood is unreliable in wet
especially in the upper panels of high piles. Reduce
places. Exterior plywood will keep its original form
dishing by placing strips between sheets of stacked
and strength when subjected to the elements. It is
plywood. Use enough strips to prevent the plywood
suitable for permanent exterior use provided it is
from sagging between strips. Dry l-inch strips are
properly protected from the elements.
Most
suitable for supporting plywood.
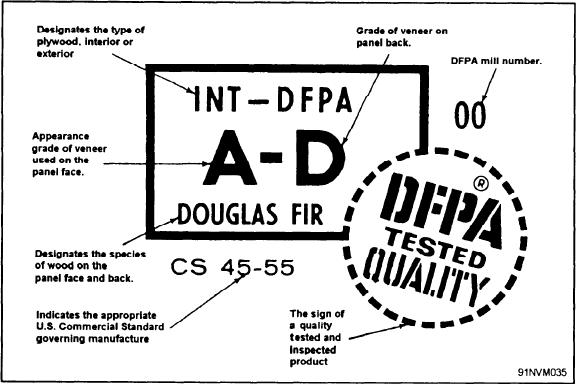
plywood is branded or stamped on the edge with the
symbol EXT. or INT. More complete information
Hardboard is known by several trade names. It
is stamped on the back of the plywood sheet. A
is wood fibers separated, treated, and then subjected
typical Douglas fir back stamp, with all symbols
to heat and heavy pressure. Hardboard is available
explained, is shown in figure 3-9.
in thicknesses from 1/16 inch to 5/6 inch. The most
common size is 4-foot by 8-foot sheets, but other
Plywood is graded by the quality of the face
sizes are available. Hardboard comes in a plain,
veneers. Grade A is the best. Grade D is the
smooth surface or in several glossy finishes. Some
poorest (fig. 3-9). Grading is based upon the
finishes imitate tile or stone. Use class B treated
number of defects, such as knotholes, pitch pockets,
hardboard where moisture resistance or strength is
and splits. It also considers the presence of streaks,
r e q u i r e d . Otherwise, class A hardboard is
discolorations, sapwood, shims, and patches in the
satisfactory.
face of the panel. Plywood has resin-impregnated
Figure 3-9.--Typical Douglas fir back stamp.
3-13

