compartment. Pulling back on a lever opens a discharge
valve and permits the flow of fuel into the piping system.
Squeezing the trip rod operation handle mounted on the
lever and moving the lever forward locks the
compartment valve and shuts off the flow of fuel.
In an emergency, the discharge valve remote control
lever, located on the left side of the discharge valve
control operating lever bank, provides a means of
locking all discharge valves. Pulling the handle causes
a release lever to trip the operating levers and locks the
valves.
OPERATION.— When operating the fuel tank
truck for discharging fuels, follow instructions
prescribed in the manufacturer’s operating manual. The
general instructions which follow are typical of the type
of fuel tank truck used in the NCF.
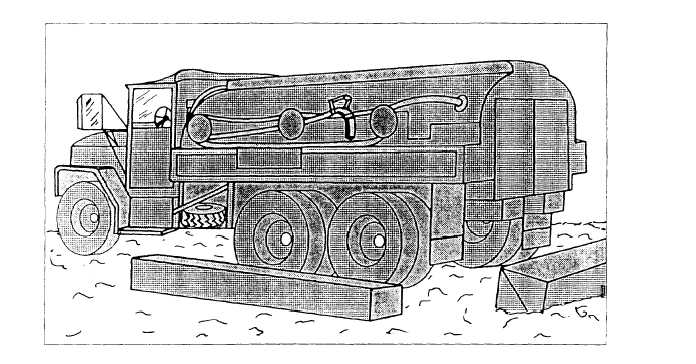
Tank trucks are used to haul and dispense fuels.
(See fig. 6-20.) The tank truck shown is equipped with
a stainless steel, 1,200-gallon tank body, which is
divided into two 600-gallon compartments (fig. 6-21).
The fuel delivery system is equipped with an upright
filter/separator and meter. Since there are only two tank
compartments, the discharge valve control has two
operating levers, as shown in figure 6-21. There is a
speed control linkage assembly that controls the speed
of the engine, power takeoff, and delivery pump.
The filter/separator in figure 6-21 is equipped with
three filter elements, three go no-go fuses, a pressure
gauge, and an automatic dump (drain) valve. The
primary function of the filter element is to collect solid
contaminants and separate water from the fuel.
The go no-go fuses shut off the fuel flow if water or
solid contaminants exceed a safe level; the shutoff of
fuel flow indicates the falters are not operating properly.
If such a malfunction exists, it must be located and
corrected and the fuses replaced before operation is
continued.
The automatic dump (drain) valve is float-operated.
The float sinks in fuel but rises in water. When water is
present in the valve housing, the float rises, the valve
opens, and the water drains away through the valve drain
tube. Open the automatic dump (drain) valve during
fueling operations.
Check the pressure differential
every day that equipment is in use and while the pump
is operating.
Close the meter drain valve, delivery pump drain
cock, and filter/separator drain valve. Open the
automatic dump (drain) valve. Enter the driver ‘S
compartment and start the engine; depress the clutch,
and put the transfer case shift lever in NEUTRAL; place
the PTO lever in the ENGAGED position; then place the
transmission gearshift lever in the gear position
recommended by the manufacturer, and release the
clutch.
Figure 6-20.-Fuel-service truck.
6-26