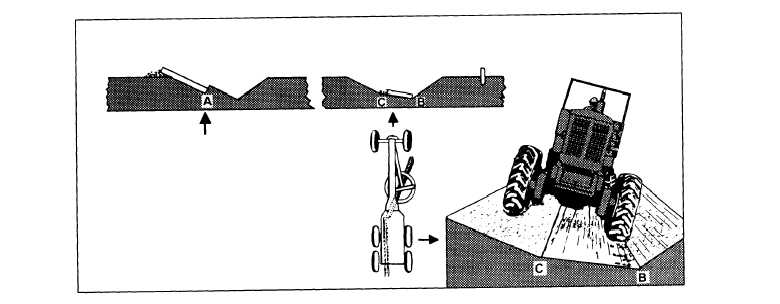
Adjustment relative to the same position. When the
distance is too short, backup and start on the opposite
shoulder with the opposite blade angle adjustment. By
repeating overlapping passes made in this manner, you
can side cast two windrows from the shoulders to the
center line where they are combined into one. The
center windrow is then spread with the blade set at 0
degrees. Material spill around the blade ends is spread
evenly among the slope of the crown.
NOTE: When grading, the operator cannot obtain
a full-visual view of a project site from the operator’s
seat. For this reason, the operator should stop and climb
off the grader periodically to take a visual look at the
work area to determine work progress and areas that
need attention.
High Bank Cuts
High bank cuts are used to cut or trim slopes on
ditches, deep cuts, and high fills. The circle and blade
are positioned vertically on the side of the grader. The
toe of the blade is angled forward of the heel.
NOTE: Read the operator’s manual for the type of
grader you are operating to receive instructions on
setting up the circle and blade for high bank-cutting
operations.
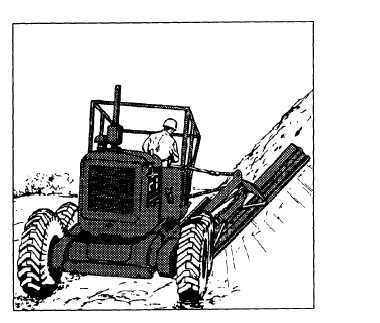
When performing high bank cuts, lean the top of the
front wheels towards the bank or slope. Move the grader
into position and set the blade on the slope (fig. 10-30).
When cutting, make light cuts with the toe of the blade.
Figure 10-29.—Flat-bottom ditch cut.
The heel of the blade does not require many adjustments.
When too much down pressure is placed on the blade,
you will lift the side off the grader or cut a gouge in the
slope. After the high bank cut is performed, clean the
cut material from the base of the slope, using the
ditching technique.
Wide Side Reach (Spreading)
A grader may be used in spreading piles of loose
material. When there is space to work around the pile,
Figure 10-30.-High bank cut.
10-13