1. Buff or roughen the tube surface to be patched
for at least 1 inch around the hole. Then clean it with
solvent. When a buffer is not available, use the
perforated cover of the kit as a scraper.
2. Apply a thin coat of rubber patching cement
evenly over the roughened surface and allow it to dry.
3. From the kit, choose a patch of the proper size
that is about 3/4 inch larger than the hole in the tube from
the kit. Remove the protective covering from the sticky
side of the patch; place the patch over the hole, and rub
it down firmly.
4. Inflate the tube with enough air to check for
leaks. If you cannot hear or feel air escaping from the
patch, you can make another check by inserting the
patched area in water. If no escaping air bubbles are
noticed, the tube may be dried and replaced in the tire
or stored.
tube, the burning material is ignited, allowed to burn,
and then removed after cooling for at least 5 minutes.
After this, examine the completed patch to see if the
edges of the patching material are attached securely to
the tube. Then install the valve core and test the tube.
Hot patches of assorted sizes are supplied in kits similar
to the cold patch kits. You will also find pressure clamps
and roughening tools in the hot patch kits.
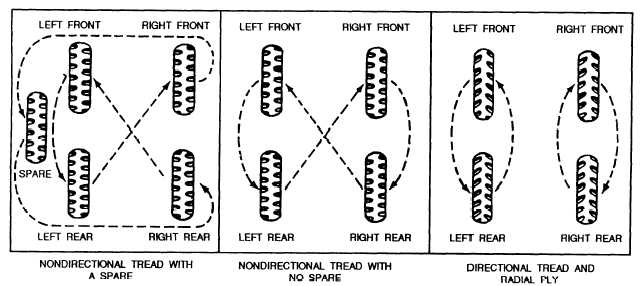
TIRE ROTATION
Rotating tires or changing them from one wheel to
another so they wear evenly is recommended by the
manufacturer. Tire rotation is performed to the
manufacturer’s specification for each vehicle.
Examples of tire rotations are shown in figure 3-37.
TIRE SAFETY
Hot Patches
Hot patches consist of a slow burning block of fuel
held in a notched metal pan on the bottom of which is a
patch of uncured rubber. To apply a hot patch, follow
the manufacturer’s instructions on the kit.
Although methods of applying patches vary with
the clamping devices provided and the shape of the
patch, you clean and roughen the tube just as you did in
applying the cold patch. When the patching unit is
placed in the notches of the patch and clamped to the
The tire shop in most commands is supervised by
the maintenance supervisor. When you are assigned to
the tire shop, the maintenance supervisor should ensure
you are briefed on tire safety by either the shop
supervisor, the tire shop foreman, or the crew leader.
People inexperienced in tire repair should only
repair tires when under the direct supervision of an
experienced person. Additionally, always refer to the
appropriate manufacturer’s manuals for directions and
instructions and remember: SAFETY COMES FIRST.
Figure 3-37.-Tire and wheel rotation.
3-20