Filter Rating
Filters are rated in several ways—absolute,
mean, and nominal. The absolute filtration rating
is the diameter in microns of the largest spherical
particle that will pass through the filter under a
certain test condition. This rating is an indication
of the largest opening in the filter element. The
mean filtration rating is the measurement of the
average size of the openings in the filter element.
The nominal filtration rating is usually interpreted
to mean the size of the smallest particles of which
90 percent will be trapped in the filter at each pass
through the filter.
Filter Elements
Filter elements generally may be divided into
two classes—surface and depth. Surface filters are
made of closely woven fabric or treated paper with
a uniform pore size. Fluid flows through the pores
of the filter material and contaminants are
stopped on the filter’s surface. This type of
element is designed to prevent the passage of a
high percentage of solids of a specific size. Depth
filters, on the other hand, are composed of layers
of fabric or fibers which provide many tortuous
paths for the fluid to flow through. The pores or
passages must be larger than the rated size of the
filter if particles are to be retained in the depth
of the media rather than on the surface.
Consequently, there is a statistical probability
that a rather large particle may pass through a
depth-type filter.
Filter elements may be of the 5-micron, woven
mesh, micronic, porous metal, or magnetic type.
The micronic and 5-micron elements have
noncleanable filter media and are disposed of
when they are removed. Porous metal, woven
mesh, and magnetic filter elements are usually
designed to be cleaned and reused.
5-MICRON NONCLEANABLE FILTER
ELEMENTS.— The most common 5-micron filter
medium is composed of organic and inorganic
fibers integrally bonded by epoxy resin and faced
with a metallic mesh upstream and downstream
for protection and added mechanical strength.
Filters of this type are not to be cleaned under
any circumstances and will be marked Disposable
or Noncleanable.
Another 5-micron filter medium uses layers
of very fine stainless-steel fibers drawn into a
random but controlled matrix. Filter elements
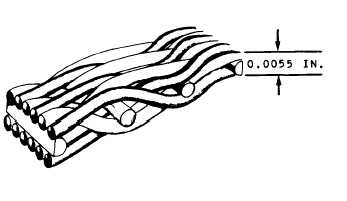
Figure 9-14.—Cross-section of a stainless steel hydraulic filter
element.
of this material may be either cleanable or
noncleanable, depending upon their construction.
WOVEN WIRE-MESH FILTER ELE-
MENTS.— Filters of this type are made of
stainless steel and are generally rated as 15 or 25
micron (absolute). Figure 9-14 shows a magnified
cross section of a woven wire-mesh filter element.
This type of filter is reusable.
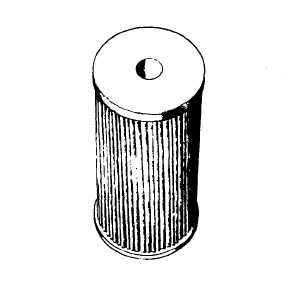
MICRONIC HYDRAULIC FILTER ELE-
MENT.— The term micronic is derived from the
word micron. It could be used to describe any
filter element; however, through usage, this term
has become associated with a specific filter with
a filtering element made of a specially treated
cellulose paper (fig. 9-15). The filter shown in
figure 9-10 is a typical micronic hydraulic filter.
This filter is designed to remove 99 percent of all
particles 10 to 20 microns in diameter or larger.
Figure 9-15.—Micronic filter element.
9-11
&