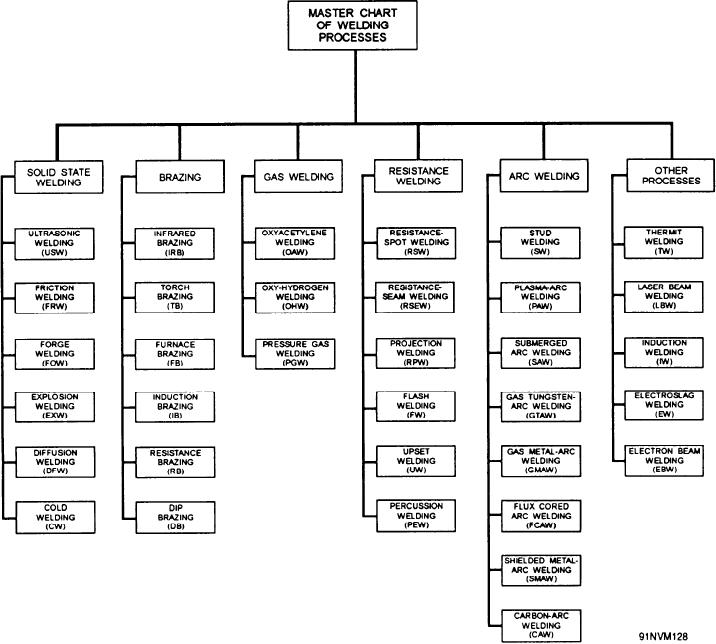
Figure 7-1.--Welding processes.
processes except brazing use temperatures high
such as acetylene or hydrogen in air or in oxygen;
enough to melt the base metals. Brazing is the
an electric arc; an electric, gas, or oil furnace; the
ONLY welding process in which the melting of the
resistance of metal to the flow of electric current; or
base metal is not necessary for coalescence. Brazing
a chemical reaction between a metal oxide and
i s similar to soldering, except that higher
finely divided aluminum. The welding processes
temperatures are used for brazing. The term
most commonly used aboard ship involve the
SOLDERING is used to describe a joining process
combustion of a fuel gas, as in oxyacetylene welding
using nonferrous filler alloys melting below 800F
and torch brazing; the use of an electric arc, as in
(427C). Soldering is NOT considered a welding
metal-arc welding; and the resistance of metal to the
process. Brazing is a welding process using
flow of electric current, as in spot welding.
nonferrous filler alloys that have a melting point
above 800F (427C) but below that of the base
The intensity of heat applied or generated at the
metal.
joint varies according to the metals being joined and
to the welding process being used. All welding
7-2