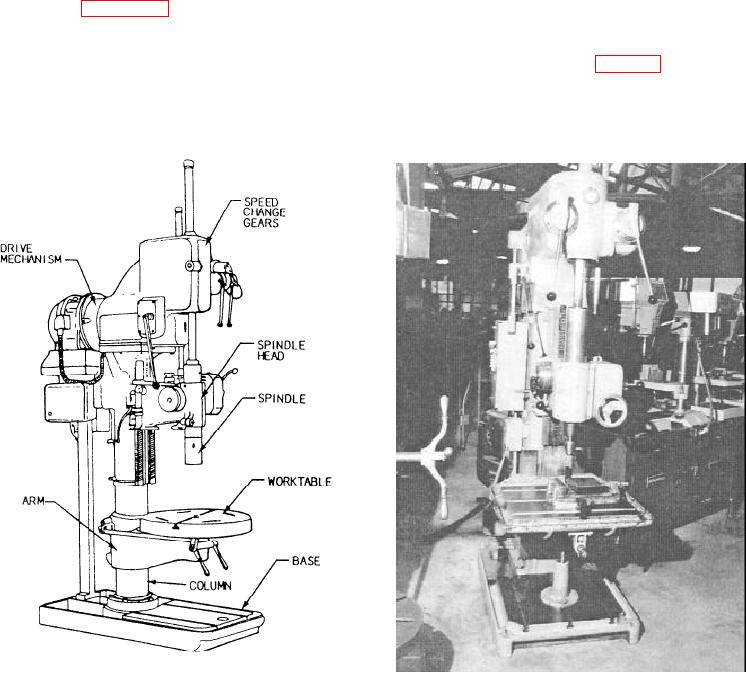
drill press and the radial drill press. These machines
The column supports the work table, the drive
have similar operating characteristics but differ in that
mechanism and the spindle head.
you position the drilling lead on the radial drill, and
The work table and arm can be swiveled around
you position the workpiece on the upright drill.
the column and can be moved up or down to adjust for
height. In addition, the work table may be rotated
UPRIGHT DRILL PRESSES
360 about its own center.
Upright drill presses discussed in this section will
The spindle head guides and supports the spindle
be the general purpose, the heavy duty, and the
and can be adjusted vertically to provide maximum
sensitive drill presses. Nearly all ships have one or
support near the spindle socket.
more of these types. They are classified primarily by
The spindle is a splined shaft with a Morse taper
the size of drill that can be used, and by the size of the
socket to hold the drill. The spline permits vertical
work that can be set up.
movement of the spindle while it is rotating.
The drive mechanism includes the motor, speed
General Purpose Drill Press (Round Column)
and feed change gears, and mechanical controls.
Heavy Duty Drill Press (Box Columns)
press is the most common type of machine found in
Navy machine shops. The basic components of this
machine are shown in the illustration.
used to drill large holes. It differs from the general
The base has a machined surface with T-slots for
purpose drill press in that the work table moves only
heavy or bulky work.
28.477
Figure 4-24.--General purpose drill press.
Figure 4-25.--Heavy duty drill press.
4-15