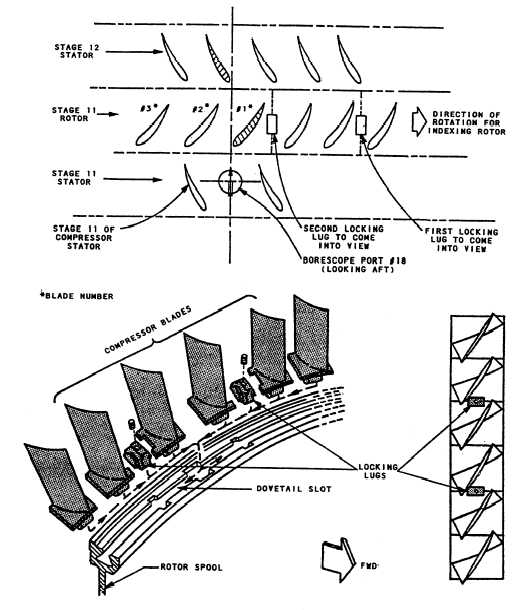
Figure 2-10.—Zero indexing the compressor rotor.
damage. Beginning with the third stage, if a slight tilting
of the blade or raising of the blade platform is observed,
suspect blade root failure.
This condition requires
suspended engine operation until the condition has been
evaluated
COMPRESSOR DAMAGE.— In tie following
paragraphs, redescribe some of the damage you may
find during an engine inspection. You can find the
condition codes used to describe engine damage in
foldout table 2-1.
Airfoil
and
Tip
Cracks.—
Cracks
in
the
compressor hardware are difficult to detect because they
are tight and shallow in depth. You can miss these subtle
defects because of deteriorated borescope optics or if
you rotate the rotor too fast. You should record all crack
information relative to the stage, area, magnitude,
direction, and adjacent blade condition.
Cracked Dovetail.— A cracked dovetail of a blade
may lead to blade loss. The location of the blade will
determine the extent of engine damage. Before the
actual catastrophic failure of the blade, the separated
crack in the dovetail will be evident by a leaning blade
platform. You can find this fault by using the borescope
to inspect each blade platform. The leaning blade
platform will be higher than the adjacent nonleaning
blades.e A “leaner” is a blade that has a crack on the aft
2-10