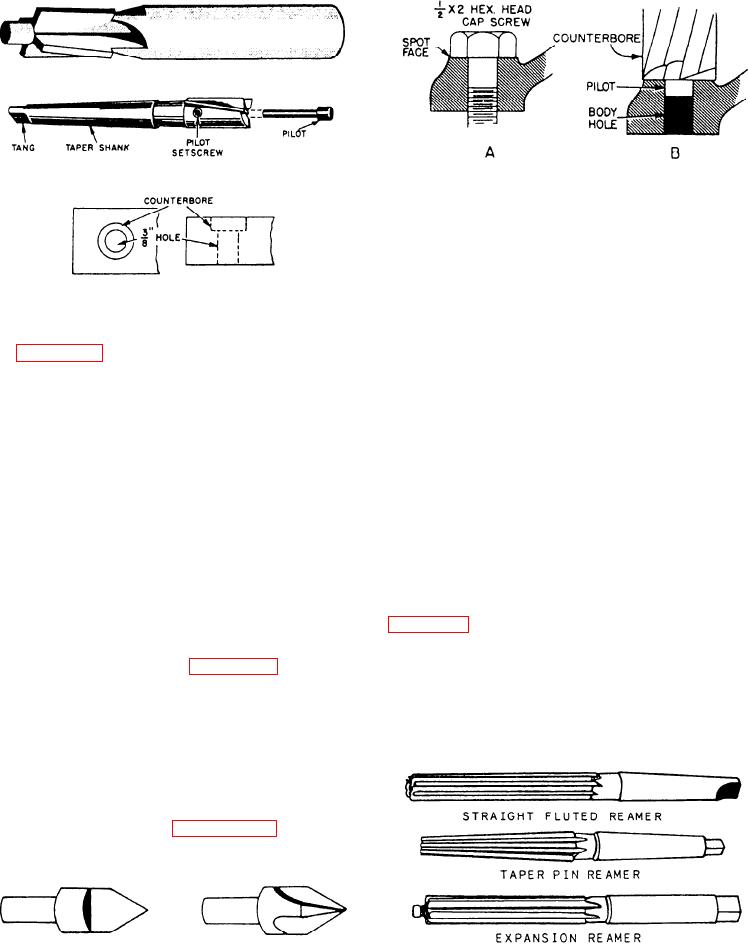
Figure 4-36.--Examples of spotfacing.
example of spotfacing and its use with fastening
devices. You will usually do this with a counterbore.
Reaming
Figure 4-34.--Two types of counterbore.
The drill press also may be used for reaming. For
Figure 4-34 shows two types of counterbores and
example, when specifications call for close
an example of a counterbored hole. The basic
tolerances, the hole must be drilled slightly undersize
difference between the counterbores illustrated is that
and then reamed to the exact dimension. Reaming
one has a removable pilot and the other does not. You
also removes burrs in a drilled hole or enlarges a
can use a conterbore with a removable pilot to
previously used hole for new applications.
counterbore a range of hole sizes by simply using the
appropriate size pilot. A counterbore with a fixed
Machine reamers have tapered shanks that fit the
pilot may be used only with holes of the same
drilling machine spindle. Be sure not to confuse them
dimensions as the pilot.
with hand reamers, which have straight shanks. You
will ruin hand reamers if you use them in a machine.
Countersinks are used to seat flathead screws
There are many types of reamers, but the ones
flush with the surface. The basic difference between
used most extensively are the straight-fluted, the taper
countersinking and counterboring is that a
pin, and the expansion types. They are illustrated in
countersink makes an angular sided recess, while the
counterbore forms straight sides. The angular point
of the countersink acts as a guide to center the tool in
The straight-fluted reamer is made to remove
the hole being countersunk. Figure 4-35 shows two
small portions of metal and to cut along the edges to
common types of countersinks.
bring a hole to close tolerance. Each tooth has a rake
angle that is comparable to that on a lathe tool.
Spotfacing is an operation that cleans up the
surface around a hole so that a fastening device can be
seated flat on the surface. This operation is
commonly required on rough surfaces that have not
been machined and on the circumference of concave
or convex workpieces. Figure 4-36 shows an
Figure 4-35.--Countersinks.
Figure 4-37.--Reamers.
4-22

