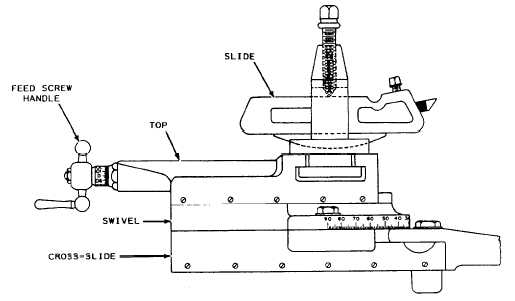
Figure 9-4.—Compound rest.
The rotating feed rod drives gears in the apron; these
gears in turn drive the longitudinal feed and crossfeed
mechanisms through friction clutches.
Some lathes do not have a separate feed rod, but use
a spline in the lead screw for the same purpose.
Lead Screw
The lead screw is used for thread cutting. It has
accurately cut Acme threads along its length that engage
the threads of half-nuts in the apron when the half-nuts
are clamped over it. The lead screw is driven by the
spindle through a gear train. Therefore, the rotation of
the lead screw bears a direct relation to the rotation of
the spindle. When the half-nuts are engaged, the
longitudinal movement of the carriage is controlled
directly by the spindle rotation. Consequently, the
cutting tool is moved a definite distance along the work
for each revolution that the spindle makes.
Crossfeed Slide
The crossfeed slide is mounted to the top of the
carriage in a dovetail and moves on the carriage at a right
angle to the axis of the lathe. A crossfeed screw allows
the slide to be moved toward or away from the work in
accurate increments.
Compound Rest
The compound rest (fig. 9-4), mounted on the
compound slide, provides a rigid adjustable mounting
for the cutting tool. The compound rest assembly has the
following principal parts:
1. The compound rest SWIVEL, which can be
swung around to any desired angle and clamped in
position. It is graduated over an arc of 90° on each side
of its center position for easier setting to the angle
selected. This feature is used for machining short, steep
tapers, such as the angle on bevel gears, valve disks, and
lathe centers.
2. The compound rest, or TOP SLIDE, which is
mounted on the swivel section on a dovetailed slide. It
is moved by the compound rest feed screw.
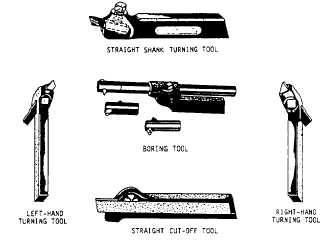
Figure 9-5.—Common types of toolholders.
9-4