CHAPTER 6
METALLURGY
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
Upon completion of this chapter; you will be able to do the following:
Explain the concepts of stress and strain in metals.
Describe the different properties of metals.
Identify the two major classes of metals.
Describe the different types offerrous and nonferrous metals.
Identify different metals by color markings, surface appearance, and identi-
fication tests.
INTRODUCTION
elements. The elements that are used as alloying sub-
stances are usually metals or metalloids. By combining
As an HT, you will be working with many different
metals and metalloids, it is possible to develop alloys
types of metals and alloys. The more knowledge you
that have the particular properties required for a given
have of metals and alloys, the better you will be able to
use.
perform your repair and maintenance duties. You
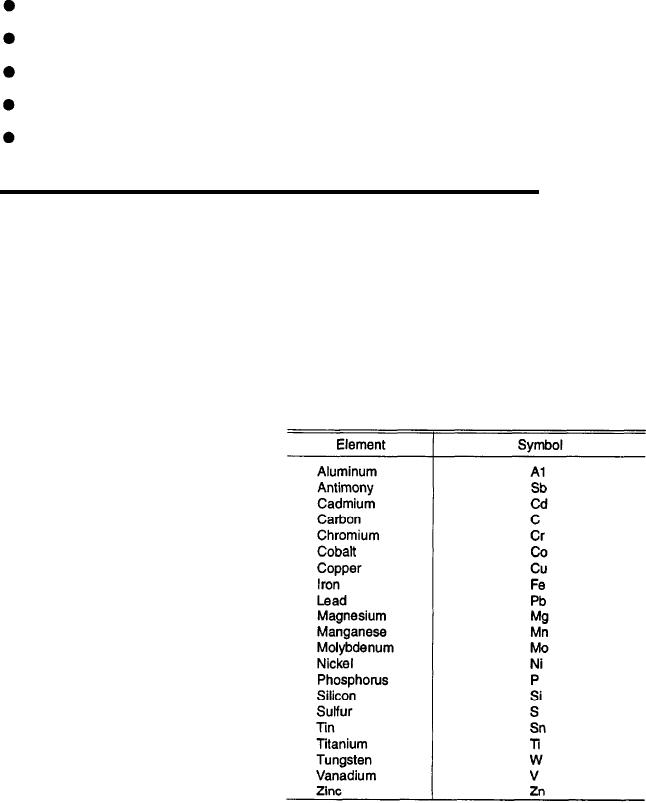
Table 6-1 lists some common metals and
should have some accurate means of identifying metals.
metalloids and gives the chemical symbol that is used
To intelligently solve welding problems, you should
to identify each element.
also have a good understanding of the internal structure
of metals, and the effects that welding (heat input) has
Table 6-1.--Symbols of Common Metals and Metalloids
on metals. This chapter will start you on your way by
giving you a basic understanding of metallurgy.
Can you define a metal? Chemical elements are
considered to be metals if they are lustrous, hard, good
conductors of heat and electricity, malleable, ductile,
and heavy. Some metals are heavier than others; some
are more malleable than others; and some are better
conductors of heat and electricity. These properties are
known as "metallic properties," and chemical elements
that possess these properties to some degree are called
metals. Chemical elements that do not possess these
chlorine, and iodine are examples of nonmetallic
chemical elements.
Chemical elements that behave sometimes like
metals and sometimes like nonmetals are often called
metalloids. Carbon, silicon, and boron are examples of
metalloids.
An alloy may be defined as a substance that has
metallic properties and is composed of two or more
6-1

