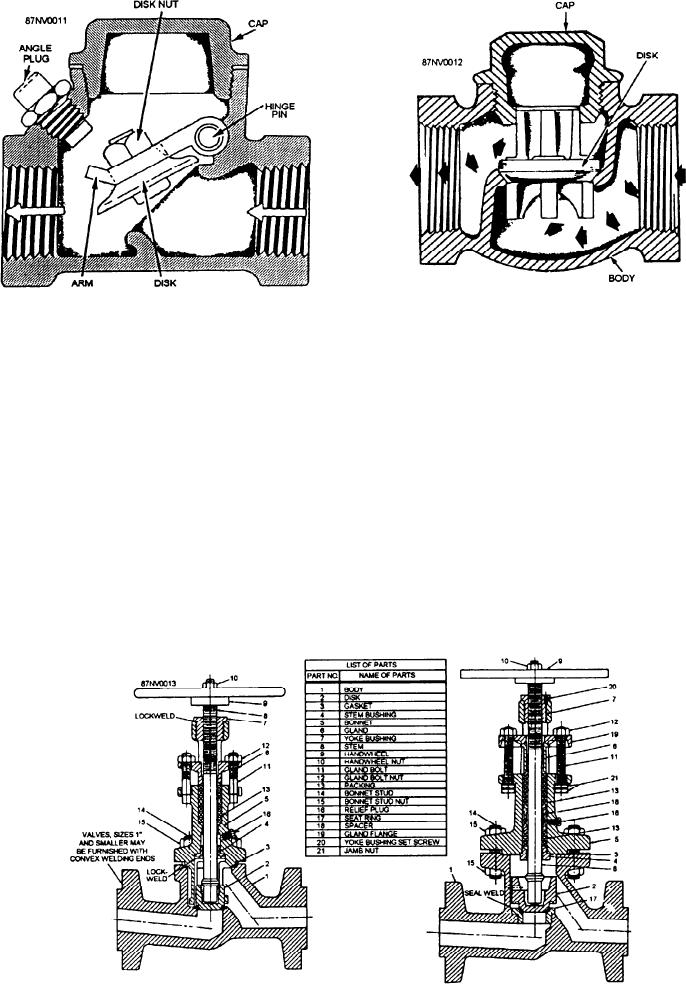
Figure 15-12.--Lift-check valve.
Figure 15-11.--Swing-check valve.
The operation of a lift-check valve (fig. 15-12) is
closely to make sure that the flow of the fluid in the
basically the same as that of the swing-check valve.
system will operate the valve in the proper manner.
The difference is that the valve disk moves in an
The port in a check valve may be closed by a disk,
up-and-down direction instead of through an arc.
a ball, or a plunger. The valve opens when the pressure
on the inlet side is greater than that on the outlet side.
STOP-CHECK VALVES
The valves also open and close automatically. They are
made with threaded, flanged, or union faces, with
As we have seen so far, most valves may be
screwed or bolted caps, and for specific pressure ranges.
classified as either stop valves or check valves.
However, some valves function either as a stop valve or
The disk of a swing-check valve (fig. 15-11) is
as a check valve, depending upon the position of the
raised as soon as the pressure in the line below the disk
valve stem. These valves are known as stopcheck
is of sufficient force. While the disk is raised,
valves.
continuous flow takes place. If for any reason the flow
is reversed, or if back pressure builds up, this opposing
The cross section of two stop-check valves is
pressure will force the disk to scat, which in turn stops
shown in figure 15-13. As you can see, this type of
the flow.
Figure 15-13.--Stop-check valves.
15-12