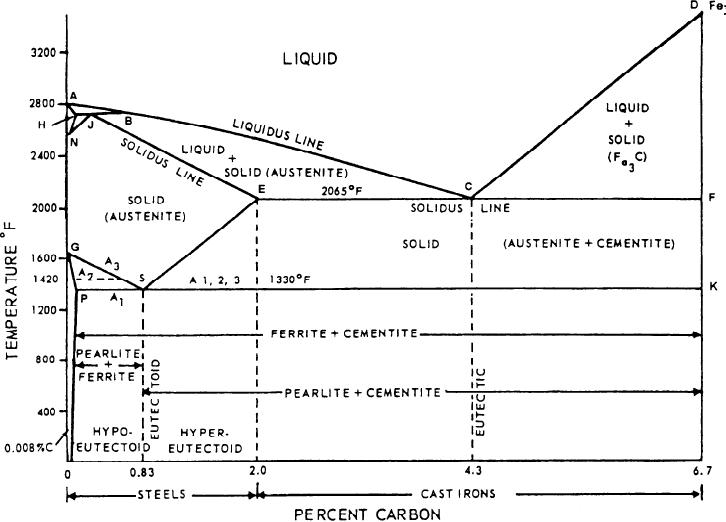
Figure 15-11.--Iron-carbon phase diagram.
cases. A wide variety of quenching oils may be used,
AIR is used for cooling some high-alloy steels and
including animal oils, fish oils, vegetable oils, and
some nonferrous metals. Both still air and circulating
mineral oils. Oils have a slower cooling rate than brine
air are used. For either method the work pieces are
or water but a faster cooling rate than air or solid
placed on racks or other suitable containers so all parts
materials. Quenching oils are usually used in the
are uniformly exposed. Air is often circulated by
temperature range of 120 to 150F.
electric fans arranged to provide uniform cooling.
The chief danger involved in quenching with oil is
Compressed air is sometimes used to concentrate the
that a hot metal piece may raise the temperature of the
cooling on particular areas. Compressed air used for this
oil to the flash point and cause it to burst into flames. A
purpose must be entirely free of moisture. Any moisture
cover should always be kept near a quenching tank that
in the air produces rapid quenching wherever it touches
is used for oil. If the oil flashes into flames, put the cover
the metal and may cause cracking or hard spots.
over the tank immediately to smother the fire.
MOLTEN LEAD at temperatures ranging from
Some water usually collects in the bottom of the oil
650 to 1,100F is often used as a first-stage quench for
tank. The water does no harm if only a small amount is
high-speed steels. A common practice is to quench
present. If enough water is present that the work extends
high-speed steel in molten lead as soon as the work is
into the water, the rapid quenching action of the water
removed from the furnace and to follow this quench by
may cause the piece to crack
cooling the part in still air to about 200F before
CAUSTIC SODA in water is used for some steels
tempering. Molten lead is not used as a quenching
that require rapid quenching. A lo-percent caustic soda
medium for nonferrous metals.
solution quenches faster than water, but slower than
MOLTEN SALT at temperatures ranging from 300
brine. Nonferrous metals are not quenched in caustic
soda solutions.
to 1,000F is sometimes used as a quenching medium
15-12