Figure 15-9.--Thermoelectric pyrometer used in heat-treating
furnance.
Figure 15-8.--Grid for heat-treating furnace.
well as measuring devices. This type of instrument can
high temperatures, and supports the heating elements
be set to develop and maintain any desired temperature
and the hearth plate.
Hearth plates are placed on the bottom of the
within the limits of the furnace design.
heating chamber to support the pieces being heated.
If you are using improvised heat-treating equip-
Hearth plates must withstand high temperatures without
ment, you will probably not have any accurate way of
sagging or scaling. They are often made of a special
measuring temperature and will have to improvise
nickel-chromium, heat-resistant alloy. If the furnace is
methods for determining temperature.
designed for the heat treatment of high-speed steels, the
It is possible to estimate the temperature of ferrous
hearth plate may be made of a carbon and silicon.
metals by noting the color changes that occur when the
Grids, usually made of iron-chromium-nickel alloy,
material is heated. This method is not practical for
keep heavy or long sections of material off the hearth
nonferrous metals since most nonferrous metals melt
plate. The use of grids ensures more uniform heating of
before they show a color change. At best, the color
the material and tends to prevent warping. A grid for an
method of judging temperatures is guesswork.
Nonetheless, you should develop some skill in using
A special type of electric furnace known as an
this technique. It may be the only method you have to
AIR-CIRCULATING FURNACE is sometimes used
estimate temperature when you do not have adequate
for stress-relieving and tempering. Air-circulating
heat-treating equipment.
furnaces are relatively low-temperature units, usually
The best way to learn to judge the temperature of
designed to operate at temperatures ranging from 275
ferrous metal by color is by heating small samples of
to 1,250F. Temperature control is both accurate and
clean, polished steel under controlled conditions. This
rapid. The maximum temperature variation is seldom
way you can check the color of the sample against the
more than plus or minus 5F, and very rapid changes to
actual temperature. Also, study the color charts that
a higher or lower temperature are possible.
relate color and temperature. Your perception of the
colors will be affected by the color and intensity of the
Temperature Measurement and Control
light in the furnace or in the room where you are
The measurement and control of temperature are
working. Use standard lighting conditions, if possible,
extremely important in all heat-treating processes.
when you must estimate the temperature of a metal by
Modern heat-treating furnaces are equipped with
observing the color. Charts are available in various
various devices for indicating (and in some cases
handbooks and textbooks on metals. Table 15-1 is a
recording) temperatures. Most furnaces are also
rough guide to the color-temperature relationships of
equipped with temperature controllers.
steel.
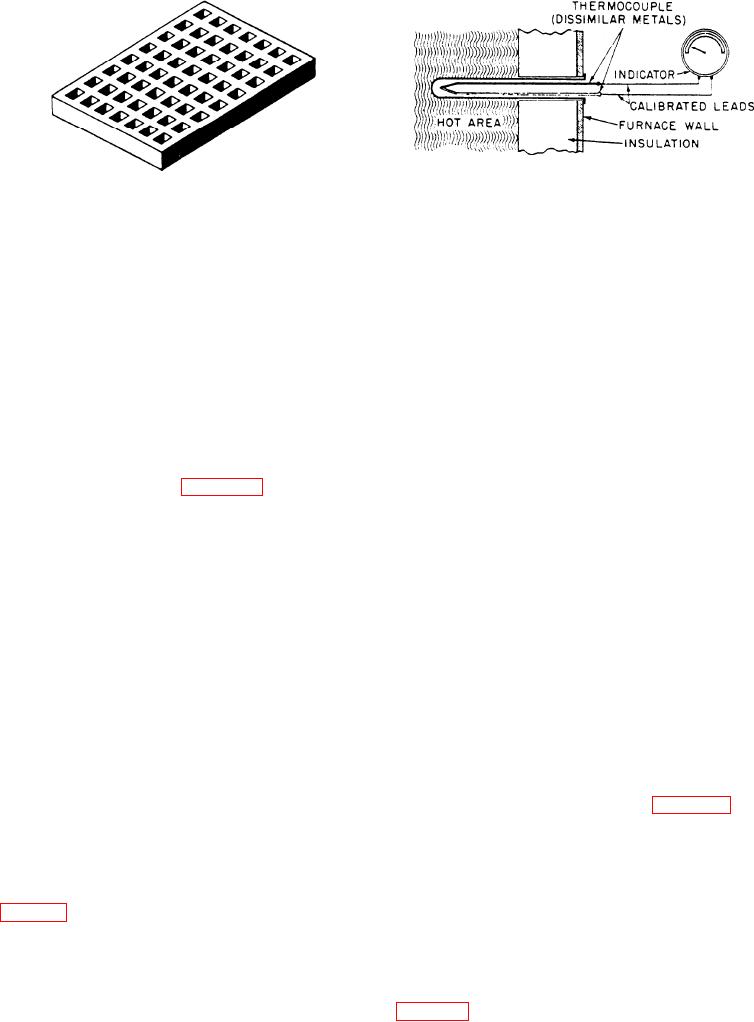
The most commonly used device for measuring the
At temperatures below those given in table 15-l)
temperature in a heat-treating furnace is the
another type of color determination can be made. If steel
THERMOELECTRIC PYROMETER. This instrument
is thoroughly cleaned and polished, the surface will
appear to change color as the material is heated. An
lead, and an indicating unit. The indicating unit is
oxide film forms on the polished surface as the steel is
calibrated in degrees Fahrenheit or Centigrade.
heated, and the oxide color corresponds to a certain
temperature. Some oxide colors for steel are given in
others indicate it and record it. Most electric furnaces
are equipped with pyrometers that are controllers as
15-8