CHARACTERISTICS OF WIRE ROPE
The main types of wire rope used by the NCF
consist of 6, 7, 12, 19, 24, or 37 wires in each strand.
Usually, the wire rope has six strands laid around the
core.
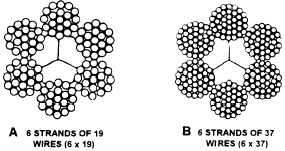
The two most common types of wire rope, 6 x 19
and 6 x 37, are shown in figure 13-6. The 6 x 19 type
(having six strands with 19 wires in each strand) is the
stiffest and strongest construction of the types of wire
rope suitable for general hoisting operations. The 6 x 37
wire rope (six strands with 37 wires in each strand) is
very flexible, making it suitable for cranes and similar
equipment where sheaves are smaller than usual. The
wires in the 6 x 37 are smaller than the wires in the
6 x 19 wire rope and, consequently, will not stand as
much abrasive wear.
Several factors must be considered whenever a wire
rope is selected for use in a particular kind of operation.
The manufacture of a wire rope which can withstand
equally well all kinds of wear and stress, it may be
subjected to, is not possible, Because of this, selecting
a rope is often a matter of compromise, sacrificing one
quality to have some other more urgently needed
characteristic.
Tensile Strength
Tensile strength is the strength necessary to with-
stand a certain maximum load applied to the rope. It
includes a reserve of strength measured in a so-called
factor of safety.
Crushing Strength
Crushing strength is the strength necessary to resist
the compressive and squeezing forces that distort the
cross section of a wire rope, as it runs over sheaves,
Figure 13-6.-A. 6 x 19 wire rope; B. 6 x 37 wire rope.
rollers, and hoist drums when under a heavy load.
Regular lay rope distorts less in these situations than
lang lay.
Fatigue Resistance
Fatigue resistance is the ability to withstand the
constant bending and flexing of wire rope that runs
continuously on sheaves and hoist drums. Fatigue
resistance is important when the wire rope must run at
high speeds. Such constant and rapid bending of the rope
can break individual wires in the strands. Lang lay ropes
are best for service requiring high fatigue resistance.
Ropes with smaller wires around the outside of their
strands also have greater fatigue resistance, since these
strands are more flexible.
Abrasion Resistance
Abrasion resistance is the ability to withstand the
gradual wearing away of the outer metal, as the rope
runs across sheaves and hoist drums. The rate of
abrasion depends mainly on the load carried by the rope
and its running speed. Generally, abrasion resistance in
a rope depends on the type of metal of which the rope is
made and the size of the individual outer wires. Wire
rope made of the harder steels, such as improved plow
steel, have considerable resistance to abrasion. Ropes
that have larger wires forming the outside of their
strands are more resistant to wear than ropes having
smaller wires which wear away more quickly.
Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance is the ability to withstand the
dissolution of the wire metal that results from chemical
attack by moisture in the atmosphere or elsewhere in the
working environment. Ropes that are put to static work,
such as guy wires, may be protected from corrosive
elements by paint or other special dressings. Wire rope
may also be galvanized for corrosion protection. Most
wire ropes used in crane operations must rely on their
lubricating dressing to double as a corrosion preventive.
MEASURING WIRE ROPE
Wire rope is designated by its diameter in inches, as
shown in figure 13-7. The correct method of measuring
the wire rope is to measure from the top of one strand
to the top of the strand directly opposite it. The wrong
way is to measure across two strands side by side.
To ensure an accurate measurement of the diameter
of a wire rope, always measure the rope at three places,
13-4