2. Lead (L)
a. The distance traveled by a thread during
one complete revolution of the worm
around its axis.
b. The lead and the linear pitch are the same
on a single-start worm. On a double-start
worm, the lead is twice the linear pitch, and
on a triple-start worm, the lead is three
times the linear pitch.
c. The number of starts multiplied by the
linear pitch equals the lead.
No. of S LP = Lend
d. The lead is needed to determine the proper
gear train ratio to set the table travel on the
milling machine and to perform work on
the lathe machine.
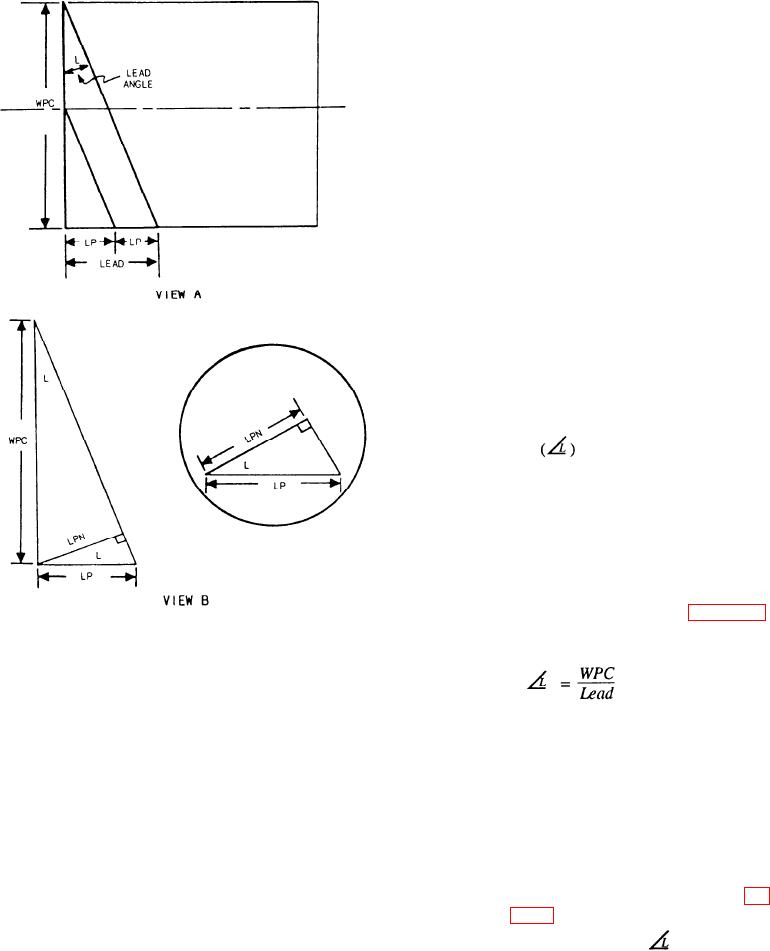
3. Lead angle
a. The angle formed by the thread and a line
drawn at a right angle to the axis of the
worm.
b. It can be found by dividing the lead into the
worm's pitch circle. The result is the
cotangent of the lead angle (fig. 14-23,
Figure 14-23.--Development of lead angle and linear pitch
view A).
(normal).
Therefore: COT
WORM AND WORM WHEEL
4. Tooth dimensions
NOMENCLATURE AND FORMULA
DEVELOPMENT
a. Linear pitch normal (LPN)
(1) Measurement of the thread (tooth) at a
You will need the following terms and formulas
right angle to its face.
when you plan and manufacture a worm and a worm
wheel:
(2) It can be found by multiplying the linear
pitch by the cosine of the lead angle (fig.
1. Linear pitch (LP)
14-23, view B).
a. The distance from a point on one thread to
LPN = LP COS
a corresponding point on the next thread.
b. This distance is measured parallel to the
(3) The tooth parts are the same in worm
and spur gears.
axis of the thread.
14-23

