specifications and standards, oxyacetylene cutting tips
are identified by three-part numbers. The first part is
the tip size (0, 1, 2, 3, and so on). The second part is
the drill size number of the orifice for the cutting
oxygen. The third part is the drill size number of the
preheat orifices. For example, the number l-62-64
identifies a number 1 tip with a cutting oxygen orifice
of drill size 62 and preheat orifices of drill size 64.
Table 8-1 gives tip numbers, orifice sizes, and
approximate cutting ranges of various sizes of oxya-
cetylene cutting tips. Cutting tips from different manu-
facturers are not interchangeable; when changing tips,
you must match the right tip with the right torch.
The tips and seats are designed and constructed to
produce a good flow of gases, to keep the tips as cool
as possible, and to produce leakproof joints. If the
joints leak, the preheat gases may mix with the cutting
oxygen or they may escape to the atmosphere.
It is very important that the orifices and passages
be kept clean and free of burrs to permit a free gas flow
and a well-shaped flame. Figure 8-12 shows four tips:
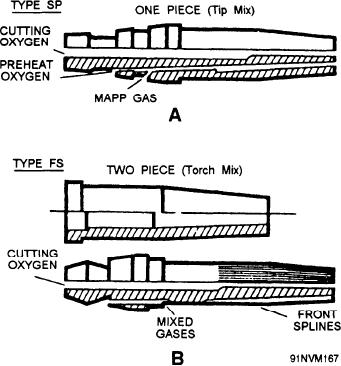
Figure 8-13.--MAPP gas cutting tips.
one that is repairable, two that need replacing, and one
in good condition. Since it is extremely important that
the sealing surfaces be kept clean and free of scratches
faster starts than the SP tips. However, two-piece tips
or burrs, the tips should be stored in a container that
will not take as much thermal abuse or physical abuse
cannot scratch the seats, preferably an aluminum or
as will one-piece tips. But in the hands of skilled
wood rack.
welders, they should last just as long as one-piece tips.
MAPP Gas Cutting Tips
Care of Tips
There are four basic types of MAPP gas cutting
In cutting operations, the stream of cutting oxygen
tips; two are designed for use with standard pressures
sometimes will blow slag and molten metal into the
and normal cutting speeds, and two for use with high
orifices and cause them to become partly clogged.
pressures and high cutting speeds. Only the standard
When this happens, you should clean the orifices
pressure tips, types SP (standard pressure) and FS (fine
thoroughly before you use the tip again; even a very
standard), will be covered here since they are the ones
small amount of slag or metal in an orifice will
that HTs will most likely use.
seriously interfere with the cutting operation. The
SP TIP.--The SP tip (fig. 8-13, view A) is a
recommendations of the torch manufacturer should be
one-piece standard-pressure tip. It is used for cutting
followed as to the size of drill or tip cleaner to use for
by hand, especially by welders who are accustomed to
cleaning the orifices. If you do not have a tip cleaner
one-piece tips. SP tips are also likely to be used in
or a drill, then you may use a piece of soft copper wire.
situations where MAPP gas is replacing acetylene as
Do not use twist drills, nails, or welding rods for
the fuel gas.
cleaning tips, as these items are likely to enlarge and
FS TIP.--The FS tip (fig. 8-13, view B) is a
distort the orifices.
two-piece, fine-spline, standard-pressure tip. It is used
The orifices of the cutting torch tip are cleaned in
for cutting by hand as well as by machine. Welders
the same manner as the single orifice of the welding
accustomed to two-piece cutting tips will use them in
torch tip. Remember that the proper technique for
hand cutting, especially in cases where MAPP gas is
cleaning the tips is to push the cleaner straight in and
replacing natural gas or propane as the fuel gas. The
FS tips will produce heavier preheating flames and
out of the orifice; be careful not to turn or twist it.
8-13

